KServe with Self-Signed Certificate Model Registry
If you are using a model registry with a self-signed certificate, you must either skip SSL verification or apply the appropriate CA bundle to the storage-initializer to create a connection with the registry. This document explains three methods that can be used in KServe, described below:
- Configure CA bundle for storage-initializer
- Global configuration
- Namespace scope configuration (Using
storage-configSecret)- JSON
- Annotation
- Skip SSL Verification
This is only available for Standard and Knative. For ModelMesh, you should add CA bundle content into the certificate parameter in storage-config.
Configure CA Bundle for Storage-Initializer
Global Configuration
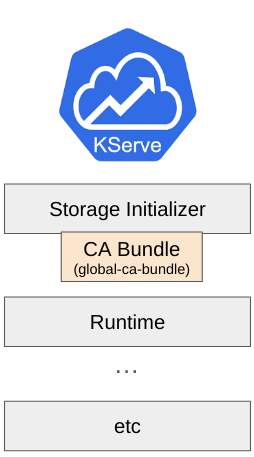
KServe uses the inferenceservice-config ConfigMap for default configuration. If you want to add a cabundle certificate for every inference service, you can set caBundleConfigMapName in the ConfigMap. Before updating the ConfigMap, you have to create a ConfigMap for the CA bundle certificate in the namespace where the KServe controller is running. The data key in the ConfigMap must be cabundle.crt.
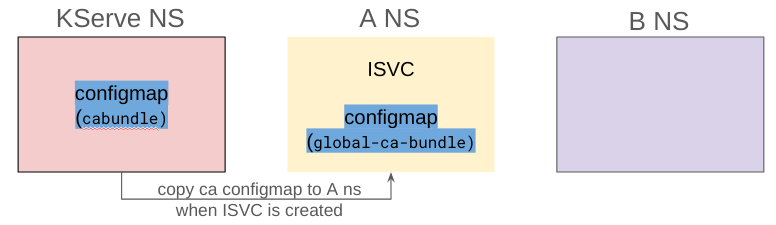
- Create a CA ConfigMap with the CA bundle certificate:
kubectl create configmap cabundle --from-file=/path/to/cabundle.crt
kubectl get configmap cabundle -o yaml
The output should look like:
apiVersion: v1
data:
cabundle.crt: XXXXX
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cabundle
namespace: kserve
- Update the
inferenceservice-configConfigMap:
storageInitializer: |-
{
...
"caBundleConfigMapName": "cabundle",
...
}
After you update this configuration, please restart the KServe controller pod to pick up the change.
When you create an inference service, the CA bundle will be copied to your user namespace and attached to the storage-initializer container.
Using Storage-Config Secret
If you want to apply the CA bundle only to a specific InferenceService, you can use a specific annotation or variable (cabundle_configmap) on the storage-config Secret used by the InferenceService.
In this case, you have to create the CA bundle ConfigMap in the user namespace before you create the InferenceService.
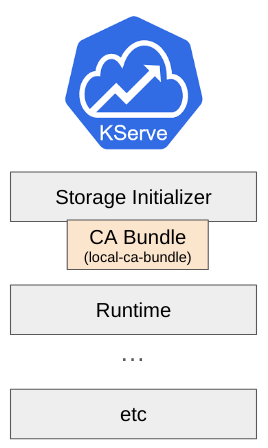
- Create a ConfigMap with the CA bundle certificate:
kubectl create configmap local-cabundle --from-file=/path/to/cabundle.crt
kubectl get configmap local-cabundle -o yaml
The output should look like:
apiVersion: v1
data:
cabundle.crt: XXXXX
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: local-cabundle
namespace: kserve-demo
- You can use one of the following approaches:
Add an annotation to storage-config Secret
apiVersion: v1
data:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: VEhFQUNDRVNTS0VZ
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: VEhFUEFTU1dPUkQ=
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
serving.kserve.io/s3-cabundle-configmap: local-cabundle
...
name: storage-config
namespace: kserve-demo
type: Opaque
Or, set a variable in the storage-config Secret
apiVersion: v1
stringData:
localMinIO: |
{
"type": "s3",
...
"cabundle_configmap": "local-cabundle"
}
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: storage-config
namespace: kserve-demo
type: Opaque
Skip SSL Verification
For testing purposes or when there is no CA bundle available, you can easily create an SSL connection by disabling SSL verification.
This can be done by adding an annotation or setting a variable in the storage-config Secret.
Add an annotation to storage-config Secret
apiVersion: v1
data:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: VEhFQUNDRVNTS0VZ
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: VEhFUEFTU1dPUkQ=
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
serving.kserve.io/s3-verifyssl: "0" # 1 is true, 0 is false
...
name: storage-config
namespace: kserve-demo
type: Opaque
Or, set a variable in the storage-config Secret
apiVersion: v1
stringData:
localMinIO: |
{
"type": "s3",
...
"verify_ssl": "0" # 1 is true, 0 is false (You can also use True/true/False/false)
}
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: storage-config
namespace: kserve-demo
type: Opaque