LLMInferenceService Configuration Guide
This guide provides detailed reference for configuring LLMInferenceService resources, including model specifications, workload patterns, router settings, and parallelism strategies.
Prerequisites: Before configuring LLMInferenceService, ensure you understand the core concepts and have installed required dependencies.
Configuration Composition Model
LLMInferenceService vs LLMInferenceServiceConfig
Similar to the relationship between InferenceService and ServingRuntime, KServe introduces LLMInferenceServiceConfig to separate configuration templates from service instances. However, the relationship and purpose differ significantly:
Comparison with InferenceService & ServingRuntime
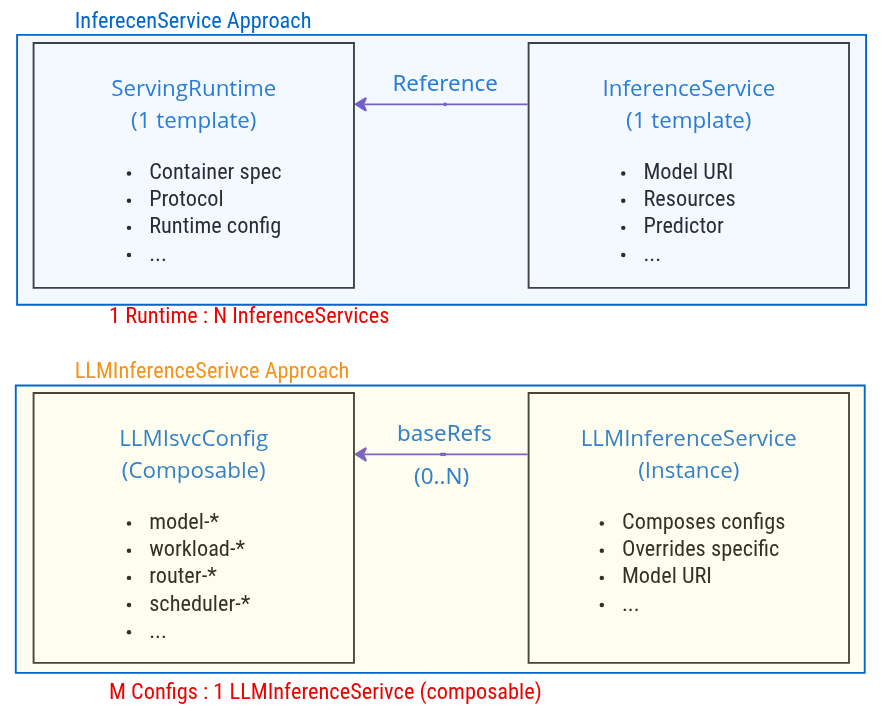
Key Differences
| Aspect | ServingRuntime → InferenceService | LLMISVCConfig → LLMInferenceService |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship | 1:N (One runtime, many services) | M:1 (Many configs, one service via composition) |
| Purpose | Runtime environment definition | Composable configuration fragments |
| Scope | Container, protocol, runtime settings | Model, workload, router, scheduler configs |
| Composition | Single runtime reference | Multiple baseRefs composition |
| Override | Limited (model URI, resources) | Flexible (any field can be overridden) |
| Granularity | Monolithic runtime definition | Modular, category-based configs |
Configuration Composition Example
# Config 1: Model configuration
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1
kind: LLMInferenceServiceConfig
metadata:
name: model-llama-3-8b
namespace: kserve
spec:
model:
uri: hf://meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
name: meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
---
# Config 2: Workload configuration
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1
kind: LLMInferenceServiceConfig
metadata:
name: workload-single-gpu
namespace: kserve
spec:
replicas: 3
template:
containers:
- name: main
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "1"
---
# Config 3: Router configuration
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1
kind: LLMInferenceServiceConfig
metadata:
name: router-managed
namespace: kserve
spec:
router:
route: {}
gateway: {}
scheduler: {}
---
# LLMInferenceService: Compose all configs
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1
kind: LLMInferenceService
metadata:
name: my-llama-service
namespace: default
spec:
baseRefs:
- name: model-llama-3-8b
- name: workload-single-gpu
- name: router-managed
# Optional: Override specific fields
replicas: 5 # Override workload-single-gpu replicas
Composition Merge Order
The merge process follows these steps:
1. Well-Known Configs (auto-injected)
Based on workload pattern, KServe automatically injects base configs:
kserve-config-llm-template(single-node)kserve-config-llm-worker-data-parallel(multi-node DP)kserve-config-llm-decode-template(prefill-decode)kserve-config-llm-scheduler(scheduler enabled)
2. Explicit BaseRefs (user-specified)
Merged in order:
- First baseRef → Second baseRef → ... → Last baseRef
- Later baseRefs override earlier ones
3. LLMInferenceService Spec (highest priority)
Final override, applied after all baseRefs.
Config Lookup Priority
getConfig(name) lookup order:
1. LLMInferenceService.namespace (same namespace) ← HIGHEST PRIORITY
2. constants.KServeNamespace (system namespace, e.g., "kserve")
Example Merge Flow
Well-Known Config (auto)
↓ (merge)
BaseRef[0] (e.g., "model-llama")
↓ (merge)
BaseRef[1] (e.g., "workload-gpu") ← overrides BaseRef[0]
↓ (merge)
BaseRef[2] (e.g., "router-managed") ← overrides BaseRef[0-1]
↓ (merge)
LLMInferenceService.spec ← HIGHEST PRIORITY, overrides all
Strategic Merge Patch
- Uses Kubernetes
strategicpatch.StrategicMergePatch - Only non-zero fields from override are merged
- Zero-valued fields (e.g., empty strings) do NOT wipe out base values
Model Specification
Basic Configuration
spec:
model:
uri: hf://meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct # Model source
name: meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct # Model name for API
Key Fields
| Field | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
uri | string | Model location | hf://meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instructs3://my-bucket/models/llama-3pvc://model-pvc/llama-3 |
name | string | Model identifier for inference requests | meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct(defaults to metadata.name) |
Workload Specification
Workload Types Overview
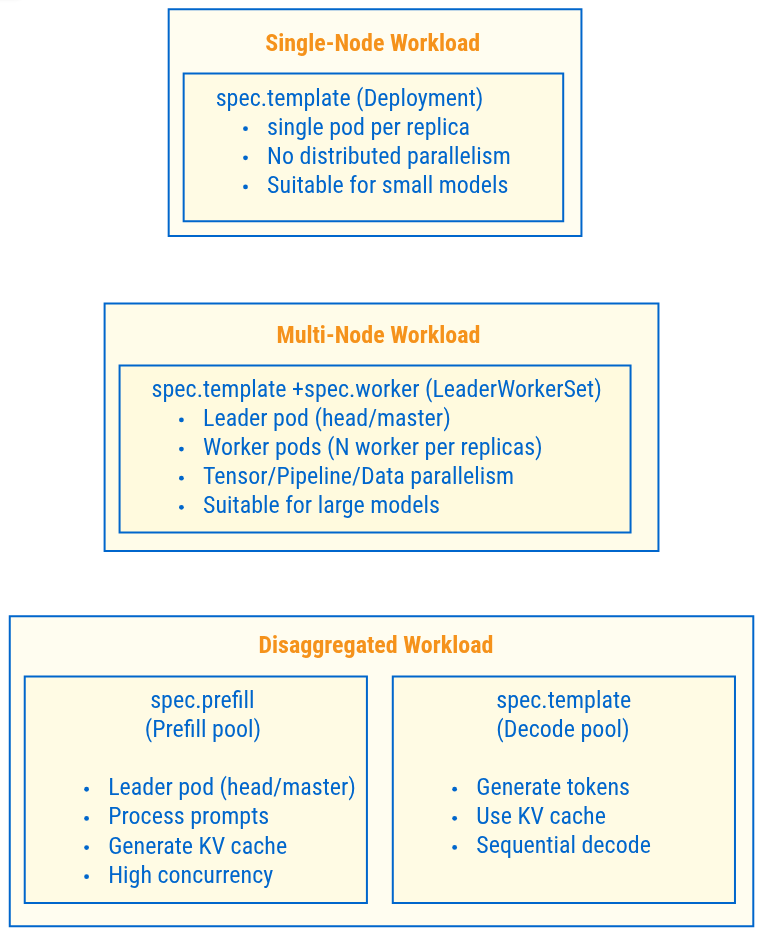
Workload Selection Logic
spec.workerpresent? → Multi-Node (LeaderWorkerSet)spec.prefillpresent? → Disaggregated (Prefill/Decode separation)- Neither present? → Single-Node (Deployment)
Single-Node Configuration
spec:
replicas: 3
template:
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "1"
cpu: "4"
memory: 32Gi
Multi-Node Configuration
spec:
replicas: 2 # Number of LeaderWorkerSet replicas
parallelism:
tensor: 4 # Tensor parallelism degree
data: 8 # Total data parallel instances
dataLocal: 4 # GPUs per node
# Result: 8 / 4 = 2 LWS replicas (overrides replicas: 2 if different)
template: # Leader pod spec
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
- "--tensor-parallel-size"
- "4"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "4"
cpu: "16"
memory: 128Gi
worker: # Worker pod spec (triggers multi-node)
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
- "--tensor-parallel-size"
- "4"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "4"
cpu: "16"
memory: 128Gi
Prefill-Decode Separation Configuration
spec:
# Decode workload (main)
replicas: 1
template:
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
- "--enforce-eager" # Decode optimization
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "1"
cpu: "8"
memory: 64Gi
# Prefill workload (separate pool)
prefill:
replicas: 2
template:
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
- "--enable-chunked-prefill" # Prefill optimization
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "2"
cpu: "16"
memory: 128Gi
Use case: Cost optimization, high throughput requirements
Router Specification
The router configuration defines how the service is exposed and how traffic is routed.
Complete Router Configuration
spec:
router:
gateway: {} # Gateway configuration
route: {} # HTTPRoute configuration
scheduler: {} # Scheduler configuration
Gateway Configuration
Managed Gateway (Default)
spec:
router:
gateway: {} # Empty object = use default gateway
KServe creates a Gateway resource automatically.
Referenced Gateway
spec:
router:
gateway:
refs:
- name: my-custom-gateway
namespace: istio-system
Use an existing Gateway instead of creating a new one.
HTTPRoute Configuration
Managed HTTPRoute (Default)
spec:
router:
route: {} # Auto-generated routing rules
Custom HTTPRoute Spec
spec:
router:
route:
http:
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- backendRefs:
- name: my-backend-service
port: 8000
Real-world Use Cases
1. Custom Timeouts (for long-running LLM inference):
spec:
router:
route:
http:
spec:
rules:
- timeouts:
request: "300s"
backendRequest: "300s"
2. URL Rewrite (multi-tenant routing):
spec:
router:
route:
http:
spec:
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /my-tenant/my-model/v1/completions
filters:
- type: URLRewrite
urlRewrite:
path:
type: ReplacePrefixMatch
replacePrefixMatch: /v1/completions
3. Service Backend (bypass InferencePool):
spec:
router:
route:
http:
spec:
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: my-custom-backend
port: 8000
Scheduler Configuration
Managed Scheduler (Default)
spec:
router:
scheduler: {} # Auto-configured scheduler
KServe creates:
- InferencePool
- InferenceModel
- Scheduler Deployment (EPP)
- Scheduler Service
Custom Scheduler with Pool
spec:
router:
scheduler:
pool:
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: workload
targetPort: 8000
Parallelism Specification
Defines distributed inference parallelism strategies for multi-node workloads.
Complete Configuration
spec:
parallelism:
tensor: 4 # Tensor parallelism (TP)
data: 8 # Data parallelism (DP)
dataLocal: 2 # Data-local parallelism (DP-local)
expert: true # Expert parallelism (EP)
dataRPCPort: 8001
Parallelism Types
Tensor Parallelism (TP)
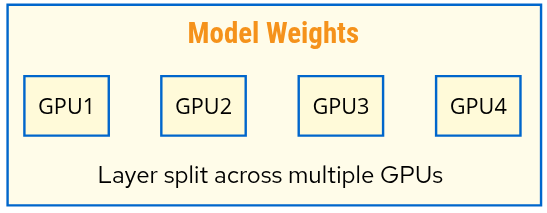
Use case: Model too large for single GPU
spec:
parallelism:
tensor: 4 # Split model across 4 GPUs
Data Parallelism (DP)
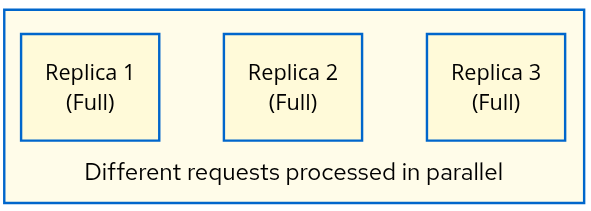
Use case: Increase throughput
spec:
parallelism:
data: 16 # 16 total replicas
dataLocal: 8 # 8 GPUs per node
# Result: 16/8 = 2 nodes
Expert Parallelism (EP)
Use case: MoE models (Mixtral, DeepSeek-R1)
spec:
parallelism:
expert: true
data: 16
dataLocal: 8
LeaderWorkerSet Size Calculation
Multi-Node Size = data / dataLocal
Example:
parallelism:
data: 16
dataLocal: 8
Result: LeaderWorkerSet.Size = 16 / 8 = 2
(1 leader + 1 worker per replica)
Complete Configuration Example
Combining all specifications:
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1alpha1
kind: LLMInferenceService
metadata:
name: llama-70b-production
namespace: production
spec:
# Model specification
model:
uri: hf://meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf
name: meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf
criticality: High
# Multi-node workload with data parallelism
parallelism:
tensor: 4
data: 8
dataLocal: 4
# Decode workload (main)
replicas: 2
template:
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
- "--tensor-parallel-size"
- "4"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "4"
rdma/roce: "1"
# Worker pods
worker:
containers:
- name: main
image: vllm/vllm-openai:latest
args:
- "--model"
- "/mnt/models"
- "--tensor-parallel-size"
- "4"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: "4"
rdma/roce: "1"
# Router configuration
router:
gateway: {}
route:
http:
spec:
rules:
- timeouts:
request: "300s"
backendRequest: "300s"
scheduler: {}
Next Steps
- Architecture Guide: Understand how components interact
- Dependencies: Install required infrastructure