Autoscale InferenceService with inference workload¶
InferenceService with target concurrency¶
Create InferenceService¶
Apply the tensorflow example CR with scaling target set to 1. Annotation autoscaling.knative.dev/target is the soft limit rather than a strictly enforced limit, if there is sudden burst of the requests, this value can be exceeded.
The scaleTarget and scaleMetric are introduced in version 0.9 of kserve and should be available in both new and old schema.
This is the preferred way of defining autoscaling options.
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample"
spec:
predictor:
scaleTarget: 1
scaleMetric: concurrency
model:
modelFormat:
name: tensorflow
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample"
annotations:
autoscaling.knative.dev/target: "1"
spec:
predictor:
tensorflow:
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
Apply the autoscale.yaml to create the Autoscale InferenceService.
kubectl apply -f autoscale.yaml
Expected Output
$ inferenceservice.serving.kserve.io/flowers-sample created
Predict InferenceService with concurrent requests¶
The first step is to determine the ingress IP and ports and set INGRESS_HOST and INGRESS_PORT
Send traffic in 30 seconds spurts maintaining 5 in-flight requests.
MODEL_NAME=flowers-sample
INPUT_PATH=input.json
SERVICE_HOSTNAME=$(kubectl get inferenceservice $MODEL_NAME -o jsonpath='{.status.url}' | cut -d "/" -f 3)
hey -z 30s -c 5 -m POST -host ${SERVICE_HOSTNAME} -D $INPUT_PATH http://${INGRESS_HOST}:${INGRESS_PORT}/v1/models/$MODEL_NAME:predict
Expected Output
Summary:
Total: 30.0193 secs
Slowest: 10.1458 secs
Fastest: 0.0127 secs
Average: 0.0364 secs
Requests/sec: 137.4449
Total data: 1019122 bytes
Size/request: 247 bytes
Response time histogram:
0.013 [1] |
1.026 [4120] |■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.039 [0] |
3.053 [0] |
4.066 [0] |
5.079 [0] |
6.093 [0] |
7.106 [0] |
8.119 [0] |
9.133 [0] |
10.146 [5] |
Latency distribution:
10% in 0.0178 secs
25% in 0.0188 secs
50% in 0.0199 secs
75% in 0.0210 secs
90% in 0.0231 secs
95% in 0.0328 secs
99% in 0.1501 secs
Details (average, fastest, slowest):
DNS+dialup: 0.0002 secs, 0.0127 secs, 10.1458 secs
DNS-lookup: 0.0002 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.1502 secs
req write: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0020 secs
resp wait: 0.0360 secs, 0.0125 secs, 9.9791 secs
resp read: 0.0001 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0021 secs
Status code distribution:
[200] 4126 responses
Check the number of running pods now, Kserve uses Knative Serving autoscaler which is based on the average number of in-flight requests per pod(concurrency). As the scaling target is set to 1 and we load the service with 5 concurrent requests, so the autoscaler tries scaling up to 5 pods. Notice that out of all the requests there are 5 requests on the histogram that take around 10s, that's the cold start time cost to initially spawn the pods and download model to be ready to serve. The cold start may take longer(to pull the serving image) if the image is not cached on the node that the pod is scheduled on.
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
flowers-sample-default-7kqt6-deployment-75d577dcdb-sr5wd 3/3 Running 0 42s
flowers-sample-default-7kqt6-deployment-75d577dcdb-swnk5 3/3 Running 0 62s
flowers-sample-default-7kqt6-deployment-75d577dcdb-t2njf 3/3 Running 0 62s
flowers-sample-default-7kqt6-deployment-75d577dcdb-vdlp9 3/3 Running 0 64s
flowers-sample-default-7kqt6-deployment-75d577dcdb-vm58d 3/3 Running 0 42s
Check Dashboard¶
View the Knative Serving Scaling dashboards (if configured).
kubectl port-forward --namespace knative-monitoring $(kubectl get pods --namespace knative-monitoring --selector=app=grafana --output=jsonpath="{.items..metadata.name}") 3000
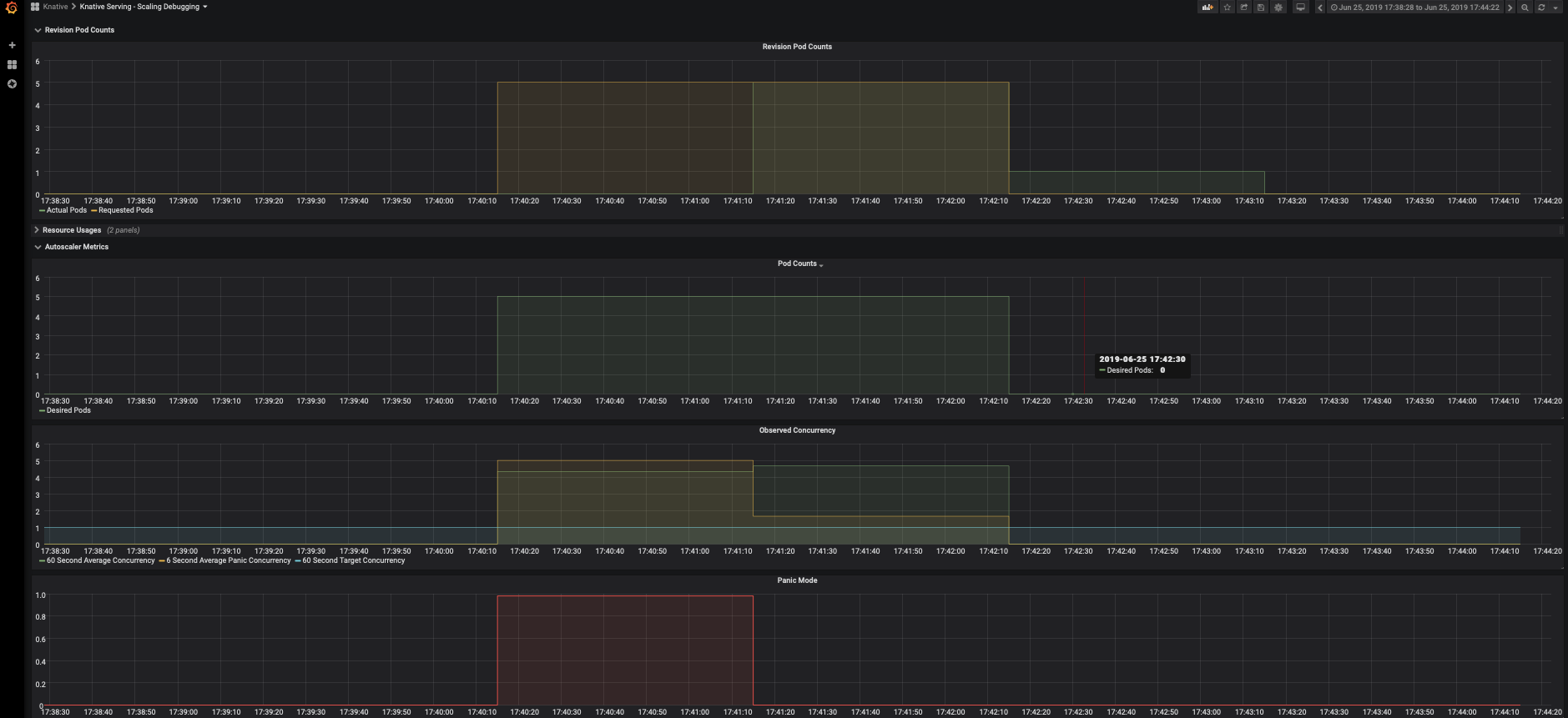
InferenceService with target QPS¶
Create the InferenceService¶
Apply the same tensorflow example CR
kubectl apply -f autoscale.yaml
Expected Output
$ inferenceservice.serving.kserve.io/flowers-sample created
Predict InferenceService with target QPS¶
The first step is to determine the ingress IP and ports and set INGRESS_HOST and INGRESS_PORT
Send 30 seconds of traffic maintaining 50 qps.
MODEL_NAME=flowers-sample
INPUT_PATH=input.json
SERVICE_HOSTNAME=$(kubectl get inferenceservice $MODEL_NAME -o jsonpath='{.status.url}' | cut -d "/" -f 3)
hey -z 30s -q 50 -m POST -host ${SERVICE_HOSTNAME} -D $INPUT_PATH http://${INGRESS_HOST}:${INGRESS_PORT}/v1/models/$MODEL_NAME:predict
Expected Output
Summary:
Total: 30.0264 secs
Slowest: 10.8113 secs
Fastest: 0.0145 secs
Average: 0.0731 secs
Requests/sec: 683.5644
Total data: 5069675 bytes
Size/request: 247 bytes
Response time histogram:
0.014 [1] |
1.094 [20474] |■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
2.174 [0] |
3.254 [0] |
4.333 [0] |
5.413 [0] |
6.493 [0] |
7.572 [0] |
8.652 [0] |
9.732 [0] |
10.811 [50] |
Latency distribution:
10% in 0.0284 secs
25% in 0.0334 secs
50% in 0.0408 secs
75% in 0.0527 secs
90% in 0.0765 secs
95% in 0.0949 secs
99% in 0.1334 secs
Details (average, fastest, slowest):
DNS+dialup: 0.0001 secs, 0.0145 secs, 10.8113 secs
DNS-lookup: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0196 secs
req write: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0031 secs
resp wait: 0.0728 secs, 0.0144 secs, 10.7688 secs
resp read: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0031 secs
Status code distribution:
[200] 20525 responses
Check the number of running pods now, we are loading the service with 50 requests per second, and from the dashboard you can see that it hits the average concurrency 10 and autoscaler tries scaling up to 10 pods.
Check Dashboard¶
View the Knative Serving Scaling dashboards (if configured).
kubectl port-forward --namespace knative-monitoring $(kubectl get pods --namespace knative-monitoring --selector=app=grafana --output=jsonpath="{.items..metadata.name}") 3000
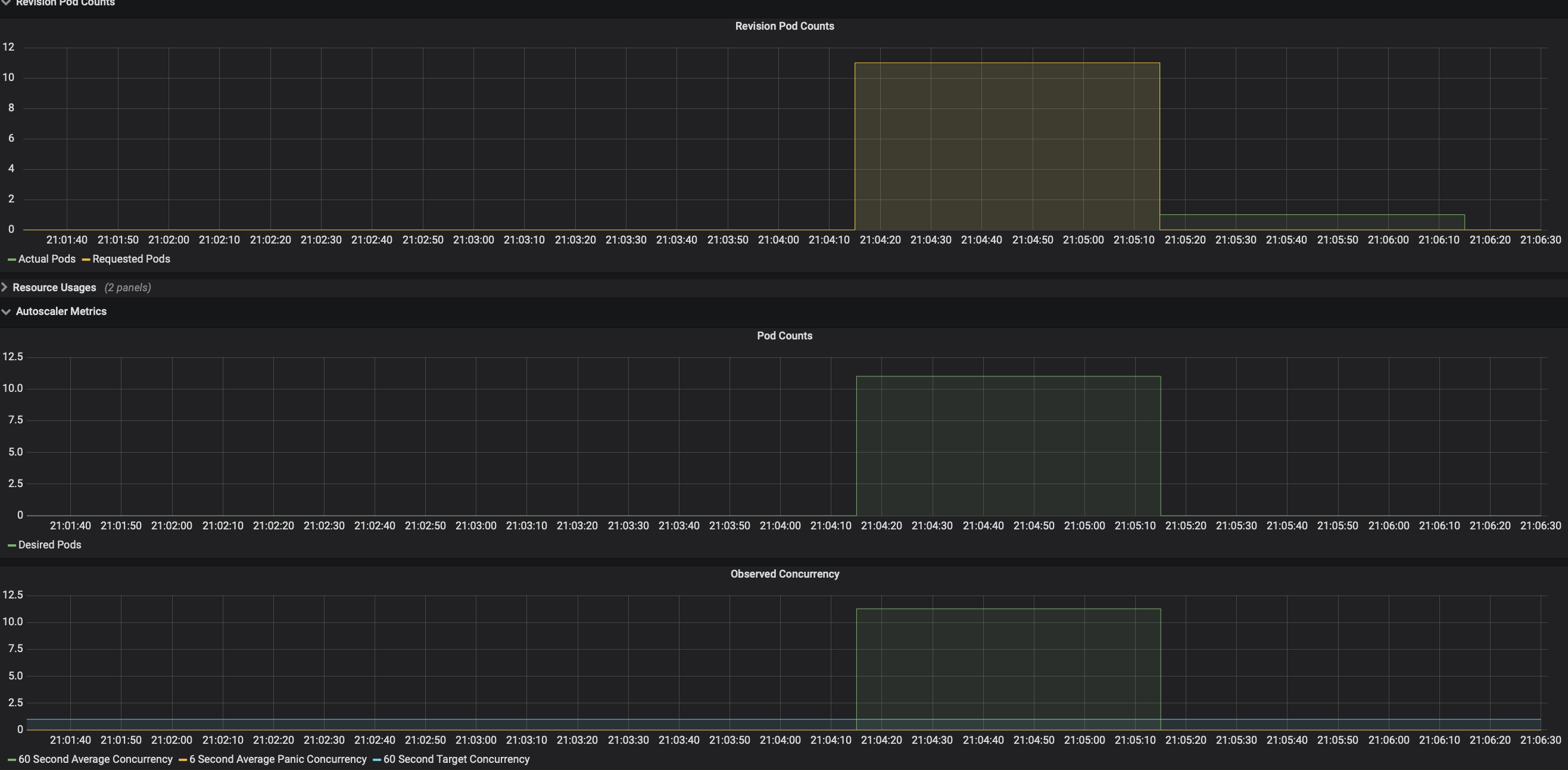
Autoscaler calculates average concurrency over 60 second window so it takes a minute to stabilize at the desired concurrency level, however it also calculates the 6 second panic window and will enter into panic mode if that window reaches 2x target concurrency. From the dashboard you can see that it enters panic mode in which autoscaler operates on shorter and more sensitive window. Once the panic conditions are no longer met for 60 seconds, autoscaler will return back to 60 seconds stable window.
Autoscaling on GPU!¶
Autoscaling on GPU is hard with GPU metrics, however thanks to Knative's concurrency based autoscaler scaling on GPU is pretty easy and effective!
Create the InferenceService with GPU resource¶
Apply the tensorflow gpu example CR
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample-gpu"
spec:
predictor:
scaleTarget: 1
scaleMetric: concurrency
model:
modelFormat:
name: tensorflow
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
runtimeVersion: "2.6.2-gpu"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample-gpu"
annotations:
autoscaling.knative.dev/target: "1"
spec:
predictor:
tensorflow:
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
runtimeVersion: "2.6.2-gpu"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
Apply the autoscale-gpu.yaml.
kubectl apply -f autoscale-gpu.yaml
Predict InferenceService with concurrent requests¶
The first step is to determine the ingress IP and ports and set INGRESS_HOST and INGRESS_PORT
Send 30 seconds of traffic maintaining 5 in-flight requests.
MODEL_NAME=flowers-sample-gpu
INPUT_PATH=input.json
SERVICE_HOSTNAME=$(kubectl get inferenceservice $MODEL_NAME -o jsonpath='{.status.url}' | cut -d "/" -f 3)
hey -z 30s -c 5 -m POST -host ${SERVICE_HOSTNAME} -D $INPUT_PATH http://${INGRESS_HOST}:${INGRESS_PORT}/v1/models/$MODEL_NAME:predict
Expected Output
Summary:
Total: 30.0152 secs
Slowest: 9.7581 secs
Fastest: 0.0142 secs
Average: 0.0350 secs
Requests/sec: 142.9942
Total data: 948532 bytes
Size/request: 221 bytes
Response time histogram:
0.014 [1] |
0.989 [4286] |■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
1.963 [0] |
2.937 [0] |
3.912 [0] |
4.886 [0] |
5.861 [0] |
6.835 [0] |
7.809 [0] |
8.784 [0] |
9.758 [5] |
Latency distribution:
10% in 0.0181 secs
25% in 0.0189 secs
50% in 0.0198 secs
75% in 0.0210 secs
90% in 0.0230 secs
95% in 0.0276 secs
99% in 0.0511 secs
Details (average, fastest, slowest):
DNS+dialup: 0.0000 secs, 0.0142 secs, 9.7581 secs
DNS-lookup: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0291 secs
req write: 0.0000 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0023 secs
resp wait: 0.0348 secs, 0.0141 secs, 9.7158 secs
resp read: 0.0001 secs, 0.0000 secs, 0.0021 secs
Status code distribution:
[200] 4292 responses
Autoscaling Customization¶
Autoscaling with ContainerConcurrency¶
ContainerConcurrency determines the number of simultaneous requests that can be processed by each replica of the InferenceService
at any given time, it is a hard limit and if the concurrency reaches the hard limit surplus requests will be buffered and must wait until
enough capacity is free to execute the requests.
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample"
spec:
predictor:
containerConcurrency: 10
model:
modelFormat:
name: tensorflow
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample"
spec:
predictor:
containerConcurrency: 10
tensorflow:
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
Apply the autoscale-custom.yaml.
kubectl apply -f autoscale-custom.yaml
Enable scale down to zero¶
KServe by default sets minReplicas to 1, if you want to enable scaling down to zero especially for use cases like serving on GPUs you can
set minReplicas to 0 so that the pods automatically scale down to zero when no traffic is received.
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample"
spec:
predictor:
minReplicas: 0
model:
modelFormat:
name: tensorflow
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "flowers-sample"
spec:
predictor:
minReplicas: 0
tensorflow:
storageUri: "gs://kfserving-examples/models/tensorflow/flowers"
Apply the scale-down-to-zero.yaml.
kubectl apply -f scale-down-to-zero.yaml
Autoscaling configuration at component level¶
Autoscaling options can also be configured at the component level. This allows more flexibility in terms of the autoscaling configuration. In a typical deployment, transformers may require a different autoscaling configuration than a predictor. This feature allows the user to scale individual components as required.
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1beta1
kind: InferenceService
metadata:
name: torch-transformer
spec:
predictor:
scaleTarget: 2
scaleMetric: concurrency
model:
modelFormat:
name: pytorch
storageUri: gs://kfserving-examples/models/torchserve/image_classifier
transformer:
scaleTarget: 8
scaleMetric: rps
containers:
- image: kserve/image-transformer:latest
name: kserve-container
command:
- "python"
- "-m"
- "model"
args:
- --model_name
- mnist
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1beta1
kind: InferenceService
metadata:
name: torch-transformer
spec:
predictor:
scaleTarget: 2
scaleMetric: concurrency
pytorch:
storageUri: gs://kfserving-examples/models/torchserve/image_classifier
transformer:
scaleTarget: 8
scaleMetric: rps
containers:
- image: kserve/image-transformer:latest
name: kserve-container
command:
- "python"
- "-m"
- "model"
args:
- --model_name
- mnist
Apply the autoscale-adv.yaml to create the Autoscale InferenceService.
The default for scaleMetric is concurrency and possible values are concurrency, rps, cpu and memory.